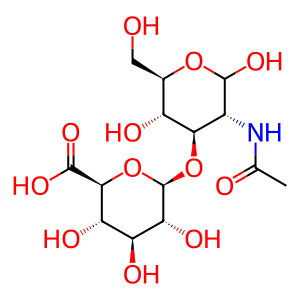
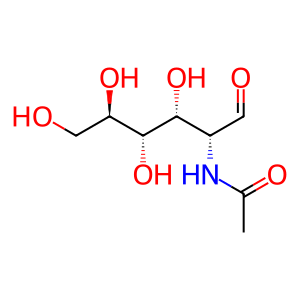
Reaction: GUSB tetramer hydrolyses GlcA-β1,3-GlcNAc
- in pathway: Hyaluronan uptake and degradation
The tetrameric lysosomal enzyme beta-glucuronidase hydrolyses glucuronate from the HA disaccharide (Oshima et al. 1987) resulting in the single sugars glucuronic acid and N-acetylglucosamine. These single sugars can exit the lysosome by an unknown mechanism. L-aspartic acid is an inhibitor of enzyme activity (Kreamer et al. 2001).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
GlcNAc [lysosomal lumen]
GlcA [lysosomal lumen]
H2O [lysosomal lumen]
GlcA-β1,3-GlcNAc [lysosomal lumen]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-2162226
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
water
beta-D-GlcpA-(1->3)-D-GlcpNAc
Reaction output - small molecules:
aldehydo-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine
D-glucuronic acid
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-2162226