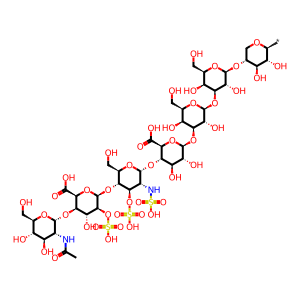
Reaction: Defective NAGLU does not hydrolyse Heparan sulfate chain(4)
- in pathway: MPS IIIB - Sanfilippo syndrome B
MPS IIIB (Sanfilippo syndrome B, Mucopolysaccharidosis IIIB, MIM:252920) is an autosomal recessive genetic disorder due to loss of function of alpha-N-acetylglucosaminidase (NAGLU; MIM:609701), normally involved in the hydrolysis of terminal non-reducing N-acetyl-D-glucosamine residues in heparan and heparan sulfate (HS). Mutations that cause severe forms of MPSIIIB are R674C or H (Zhao et al. 1998), R297X (Yogalingam & Hopwood 2001, Zhao et al. 1998) and R626X (Beesley et al 2004).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
H2O [lysosomal lumen]
Heparan sulfate chain(4) [lysosomal lumen]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-2263496
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
water
alpha-D-GlcNAc-(1->4)-beta-D-IdoA2S-(1->4)-alpha-D-GlcNS3S-(1->4)-beta-D-GlcA-(1->3)-beta-D-Gal-(1->3)-beta-D-Gal-(1->4)-beta-D-Xyl-yl group
Reaction output - small molecules:
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-2263496