Reaction: PIP3 recruits AKT to the membrane
- in pathway: PIP3 activates AKT signaling
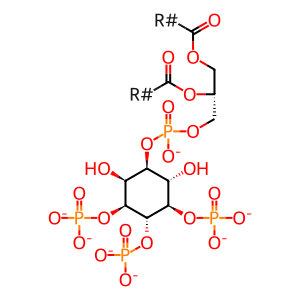
PIP3 generated by PI3K recruits AKT (also known as protein kinase B) to the membrane, through its PH (pleckstrin-homology) domains. The binding of PIP3 to the PH domain of AKT is the rate-limiting step in AKT activation (Scheid et al. 2002). In mammals there are three AKT isoforms (AKT1-3) encoded by three separate genes. The three isoforms share a high degree of amino acid identity and have indistinguishable substrate specificity in vitro. However, isoform-preferred substrates in vivo cannot be ruled out. The relative expression of the three isoforms differs in different mammalian tissues: AKT1 is the predominant isoform in the majority of tissues, AKT2 is the predominant isoform in insulin-responsive tissues, and AKT3 is the predominant isoform in brain and testes. All 3 isoforms are expressed in human and mouse platelets (Yin et al. 2008; O'Brien et al. 2008). Note: all data in the pathway refer to AKT1, which is the most studied.
Reaction - small molecule participants:
PI(3,4,5)P3 [plasma membrane]
PI(3,4,5)P3 [plasma membrane]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-2317332
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
1-phosphatidyl-1D-myo-inositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate(7-)
1-phosphatidyl-1D-myo-inositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate(7-)
Reaction output - small molecules:
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-2317332