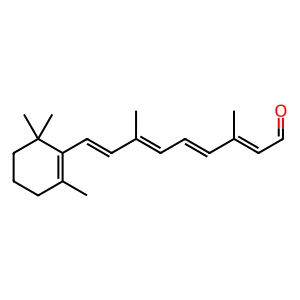
Reaction: at-retinyl is hydrolysed from R* to release atRAL
- in pathway: The retinoid cycle in cones (daylight vision)
After the very fast isomerisation of the 11-cis-retinyl (11c-retinyl) group to the all-trans-retinyl (at-retinyl) group attached to opsins by light stimulation, slower events lead to exposure of at-retinyl group to the aqueous environment, resulting in the hydrolysis of the Schiff base linkage. Although other intermediate products are formed, the ultimate result is the release of all-trans-retinal (atRAL) from opsins, with apo-opsins being reformed (Baumann & Bender 1973). These series of slow decay reactions are called light bleaching of opsin and ends when atRAL, which can diffuse across membranes to the cytosol, is reduced to all-trans-retinol (atROL)
Reaction - small molecule participants:
atRAL [cytosol]
H2O [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-2466085
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
water
Reaction output - small molecules:
all-trans-retinal
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-2466085