Reaction: FNTA:FNTB transfers FARN to GNGT1
Prenylation is the process of post-translational addition of hydrophobic groups to proteins and is thought to help anchor proteins to cellular membranes. Farnesylation is a type of prenylation, where a farnesyl group (donated from farnesyl diphosphate, FPP) is added to a cysteine residue on a protein. The enzyme mediating this transfer is farnesyltransferase (FNT). FNT is a heterodimer comprising an alpha subunit (common to another prenylating enzyme called geranylgeranyltransferase, GGT) and a unique beta subunit (Long et al. 2001, Bell et al. 2002, deSolms et al. 2003). This complex recognises the CAAX box (C is the cysteine, A is any aliphatic amino acid, and X determines which enzyme acts on the protein) at the C-terminus of the target protein, in this case, the gamma subunit of transducin (GNG1) (Omer at al. 1993).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
PPi [cytosol]
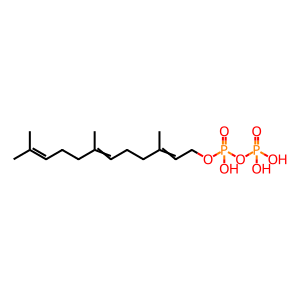
FPP [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-2530501
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
farnesyl diphosphate
Reaction output - small molecules:
diphosphate(3-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-2530501