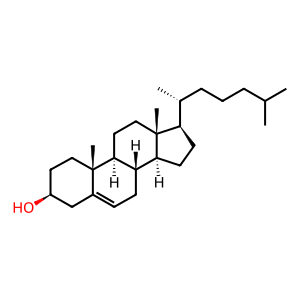
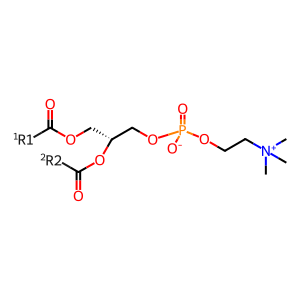
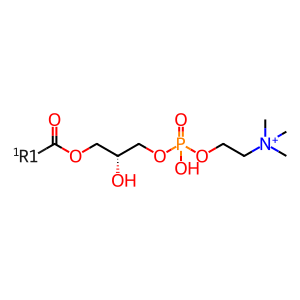
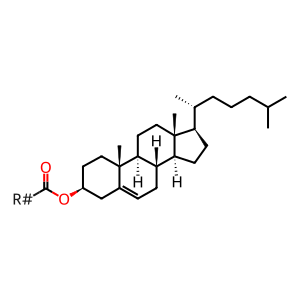
Reaction: cholesterol + phosphatidylcholine (lecithin) => cholesterol ester + 2-lysophosphatidylcholine (lysolecithin)
- in pathway: HDL remodeling
LCAT activated by apoA-I catalyzes the reaction of cholesterol and phosphatidylcholine to yield cholesterol esterified with a long-chain fatty acid and 2-lysophosphatidylcholine. While this reaction was first studied in vitro using purified proteins in solution, it occurs in vivo on the surfaces of HDL particles where transiently-bound LCAT is activated by HDL-associated apoA-I protein and consumes HDL-associated cholesterol and phosphatidylcholine. The cholesterol ester reaction product is strongly associated with the HDL particle because of its increased hydrophobicity, while the 2-lysophosphatidylcholine product is released from the particle (Fielding et al. 1972 [2 references]; Adimoolam et al. 1998).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
1-acyl LPC [extracellular region]
CHEST [extracellular region]
CHOL [extracellular region]
PC [extracellular region]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-264695
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
cholesterol
1,2-diacyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine
Reaction output - small molecules:
1-O-acyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine(1+)
cholesteryl ester
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-264695