Reaction: ABCG1-mediated transport of intracellular cholesterol to the cell surface
- in pathway: ABC transporters in lipid homeostasis
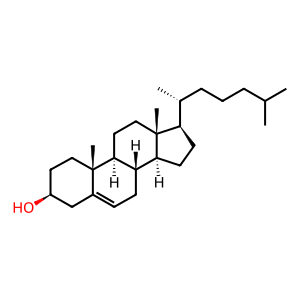
In an ATP-dependent reaction, ABCG1 mediates the movement of intracellular cholesterol to the extracellular face of the plasma membrane. In a tissue culture model system, the active form of ABCG1 is predominantly a tetramer (Vuaghan and Oram 2005). The number of lipid molecules transported per ATP consumed is not known.
Reaction - small molecule participants:
Pi [cytosol]
ADP [cytosol]
CHOL [plasma membrane]
H2O [cytosol]
CHOL [transport vesicle membrane]
ATP [cytosol]
Pi [cytosol]
ADP [cytosol]
CHOL [plasma membrane]
H2O [cytosol]
CHOL [transport vesicle membrane]
ATP [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-266082
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
water
cholesterol
ATP(4-)
water
cholesterol
ATP(4-)
Reaction output - small molecules:
hydrogenphosphate
ADP(3-)
cholesterol
hydrogenphosphate
ADP(3-)
cholesterol
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-266082