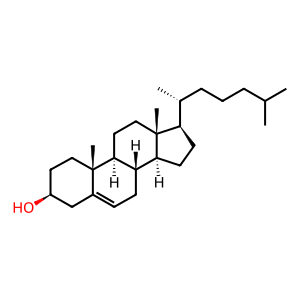
Reaction: Discoidal HDL binds membrane-associated free cholesterol
- in pathway: HDL remodeling
Extracellular discoidal HDL particles interact with cholesterol-rich membrane patches formed through the action of ABCG1 (Vaughan and Oram 2005). In the body this reaction is a key step in the process of reverse cholesterol transport, by which excess cholesterol is recovered from cells such a macrophages and transported ultimately to the liver. At a molecular level, it is one of the steps in the transformation of discoidal (small nascent) HDL particles into spherical ones, distinct from the similar reaction in which cholesterol is transferred to lipid-free apoA-I protein (Oram and Vaughan 2006; Kontush and Chapman 2006).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
CHOL [plasma membrane]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-266089
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
cholesterol
Reaction output - small molecules:
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-266089