Reaction: Spherical HDL binds membrane-associated free cholesterol and phospholipids
- in pathway: HDL remodeling
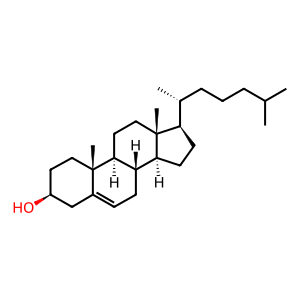
Spherical (mature) HDL particles can acquire additional molecules of free cholesterol (CHOL) and phospholipid (PL) from cell membranes. In the body, this is an important step in the so-called reverse cholesterol transport process in which excess CHOLl, notably in foam cells in atherosclerotic plaques, is transferred to HDL particles and transported ultimately to the liver. While studies in vitro and in mutant mice indicate that PLTP (phospholipid transfer protein) plays a major role in this process, its molecular details remain unclear (Oram et al. 2003) and the reaction is annotated here as the addition of two molecules each of CHOL and PL to a spherical HDL to create an "enlarged" spherical HDL.
Reaction - small molecule participants:
CHOL [plasma membrane]
PL [plasma membrane]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-266299
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
cholesterol
phospholipid
Reaction output - small molecules:
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-266299