Reaction: HLCS biotinylates PC:Mn2+
- in pathway: Biotin transport and metabolism
Biotin (Btn) acts as a coenzyme to 4 carboxylases which exist in their inactive apo forms. In the cytosol, these apo-carboxylases are biotinylated to their active halo forms by the activity of biotin-protein ligase (HCLS) (Ingaramo & Beckett 2012, Hiratsuka et al. 1998, Bailey et al. 2010). HCLS is localised to the cytosol and mitochondrion so can perform this activity in either of these locations. Defects in HLCS causes holocarboxylase synthetase deficiency (HLCS deficiency aka biotin-responsive multiple carboxylase deficiency; MIM:253270). HLCS deficiency is an autosomal recessive disorder whereby deficient HLCS activity results in reduced activity of multiple carboxylases. Symptoms include metabolic acidosis, organic aciduria, lethargy, hypotonia, convulsions and dermatitis (Suzuki et al. 2005). Pyruvate carboxylase (PC) is homotetrameric, binds 1 Mn2+ and 1 Btn per PC subunit (Xiang & Tong 2008). The exact order in which this complex is constructed is unknown.
Reaction - small molecule participants:
PPi [cytosol]
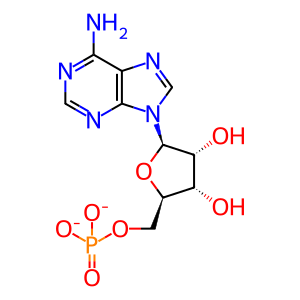
AMP [cytosol]
ATP [cytosol]
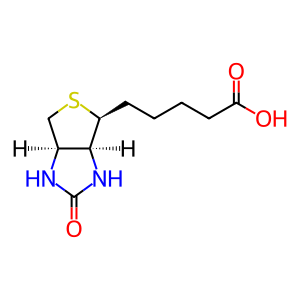
Btn [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-2993802
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
ATP(4-)
biotin
Reaction output - small molecules:
diphosphate(3-)
adenosine 5'-monophosphate(2-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-2993802