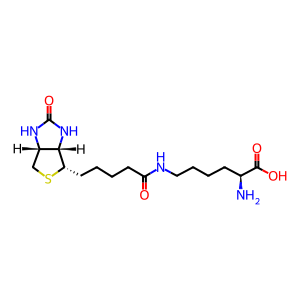
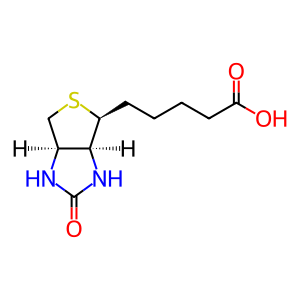
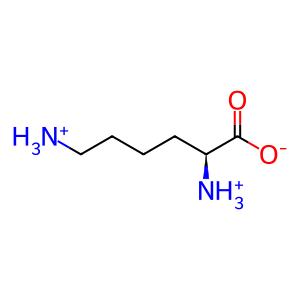
Reaction: Extracellular BTD hydrolyses BCTN
- in pathway: Biotin transport and metabolism
Human biotinidase (BTD, EC 3.5.1.12) (Cole et al. 1994) catalyzes the hydrolysis of biocytin (BCTN, aka biotinyl-lysine), a product of biotin dependent carboxylase degradation, to biotin (Btn) and lysine. As a result, Btn is again available to be used in the biotinylation of apo-carboxylases in the mitochondrion. BTD is both secreted from various cells and localised in the mitochondria (Wolf & Jensen 2005). BTD deficiency, an autosomal recessive disorder, results in a secondary Btn deficiency that leads to juvenile onset multiple carboxylase deficiency (MIM:253260) (Wolf et al. 1983).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
Btn [extracellular region]
L-Lys [extracellular region]
BCTN [extracellular region]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-3076905
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
biocytin
Reaction output - small molecules:
biotin
L-lysinium(1+)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-3076905