Reaction: MMACHC dealkylates RCbl
- in pathway: Cobalamin (Cbl) metabolism
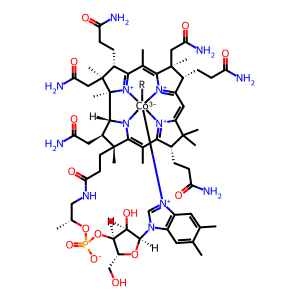
MMACHC (Methylmalonic aciduria and homocystinuria type C protein, aka cblC protein) catalyses the removal of the "R" group (formally, the upper axial ligand) from RCbl (eg dealkylation of AdoCbl and MeCbl) coupled to its reduction to cob(I)alamin (+1 oxidation state) (Hannibal et al. 2009; Kim et al. 2009; Koutmos et al. 2011).
Defects in MMACHC cause methylmalonic aciduria and homocystinuria type cblC (MMAHCC; MIM:277400). MMAHCC is the most common disorder of Cbl metabolism and is characterised by decreased levels of the coenzymes adenosylcobalamin (AdoCbl) and methylcobalamin (MeCbl). Affected individuals may have developmental, haematologic, neurologic, metabolic, ophthalmologic, and dermatologic clinical findings (Lerner Ellis et al. 2006).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
H+ [cytosol]
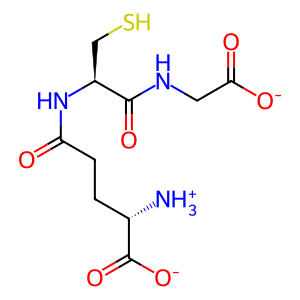
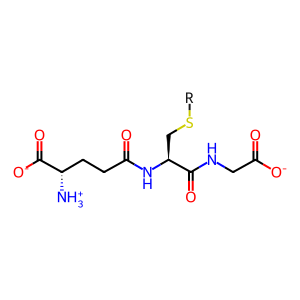
R-GSH [cytosol]
GSH [cytosol]
RCbl [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-3095889
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
glutathionate(1-)
R-cob(III)alamin
Reaction output - small molecules:
hydron
S-substituted glutathione(1-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-3095889