Reaction: MMAB adenosylates cob(I)alamin
- in pathway: Cobalamin (Cbl) metabolism
In a complex reaction, MMAB (mitochondrial cob(I)yrinic acid a,c diamide adenosyltransferase) homotrimer mediates the conversion of cob(II)alamin to a transient cob(I)alamin form which is then adenosylated to form adenosylcobalamin (AdoCbl) (Banerjee et al. 2021; Campanello et al. 2018; Fan & Bobik 2008, Leal et al. 2003; Stich et al. 2005). Defects in MMAB cause methylmalonic aciduria type cblB (MMAB aka methylmalonic aciduria type B or vitamin B12 responsive methylmalonicaciduria of cblB complementation type; MIM:251110). Affected individuals have potentially life-threatening methylmalonic aciduria and metabolic ketoacidosis, despite a functional methylmalonyl CoA mutase (Dobson et al. 2002).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
FAD [mitochondrial matrix]
PPP [mitochondrial matrix]
H+ [mitochondrial matrix]
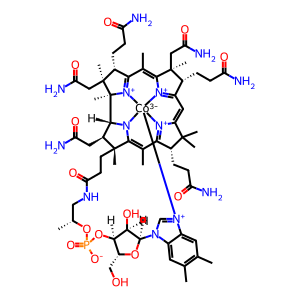
AdoCbl [mitochondrial matrix]
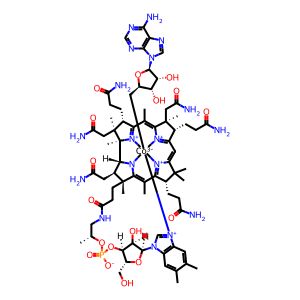
cob(II)alamin [mitochondrial matrix]
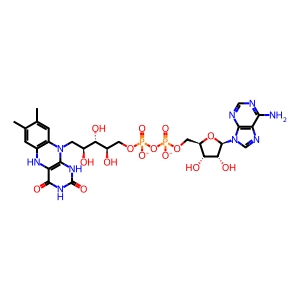
ATP [mitochondrial matrix]
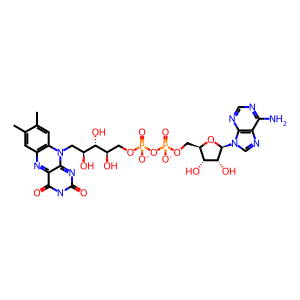
FADH2 [mitochondrial matrix]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-3159253
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
cob(II)alamin
ATP(4-)
FADH2(2-)
Reaction output - small molecules:
FAD(3-)
triphosphate ion
hydron
cobamamide
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-3159253