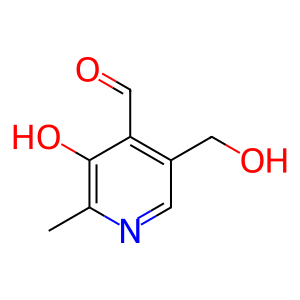
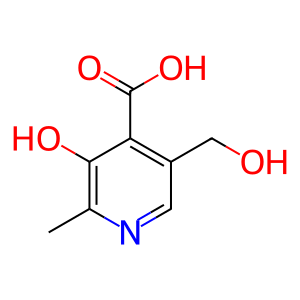
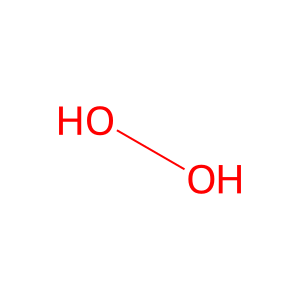
Reaction: AOX1 oxidises PXL to PDXate
- in pathway: Vitamin B6 activation to pyridoxal phosphate
Aldehyde oxidase (AOX1) is a complex molybdo-flavoprotein that belongs to the xanthine oxidase family. It is active as a homodimer, with each monomer binding two distinct [2Fe2S] clusters, FAD and the molybdenum cofactor. AOX1 plays an important role in the metabolism of drugs based on its broad substrate specificity oxidising aromatic aza-heterocycles and aldehydes (Hartmann et al. 2012).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
PDXate [cytosol]
H2O2 [cytosol]
H2O [cytosol]
O2 [cytosol]
PXL [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-3204311
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
water
dioxygen
pyridoxal
Reaction output - small molecules:
4-pyridoxic acid
hydrogen peroxide
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-3204311