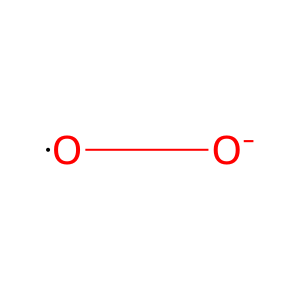
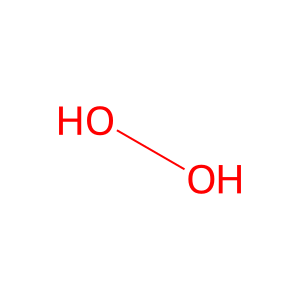
Reaction: SOD2 catalyzes 2H+ + 2O2.- => O2 + H2O2 (mitochondrial matrix)
- in pathway: Detoxification of Reactive Oxygen Species
Mn superoxide dismutase (SOD2) is located in the mitochondrial matrix where it catalyzes the reaction of two molecules of superoxide (O2-.) to form one molecule of oxygen (O2) and one molecule of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). Data from mouse liver indicate that respiratory complex I leaks superoxide into the matrix and respiratory complex III leaks superoxide into both the matrix and the intermembrane space (Muller et al. 2004). Because of its negative charge superoxide is unable to cross membranes, however hydrogen peroxide, a product of SOD2, is released from mitochondria to the cytosol in proportion to the proton potential (inferred from rat heart mitochondria in Boveris et al. 2006, Korshunov et al. 1997).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
O2 [mitochondrial matrix]
H2O2 [mitochondrial matrix]
H+ [mitochondrial matrix]
O2.- [mitochondrial matrix]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-3299680
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
hydron
superoxide
Reaction output - small molecules:
dioxygen
hydrogen peroxide
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-3299680