Reaction: ATF2 acetylates histone H2B, H4
- in pathway: HATs acetylate histones
ATF2 (activating transcription factor 2) is a basic leucine zipper (bZIP) protein and member of the activator protein-1 (AP-1) family (Wagner et al. 2001). The basic region of ATF2 binds DNA while the leucine zipper region allows dimerization with partners. ATF2 is a histone acetyltransferase (HAT), which specifically acetylates histones H2B and H4 in vitro. ATF2 is sequentially phosphorylated on threonine residues T69 and T71 by protein kinases ERK1/2 and p38 (van Dam et al. 1995, Livingstone et al. 1995, Ouwens et al. 2002, Baan et al. 2009). This phosphorylated form has increased HAT activity (Kawasaki et al. 2000).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
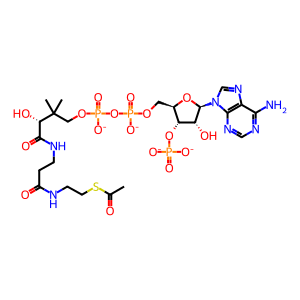
CoA-SH [nucleoplasm]
Ac-CoA [nucleoplasm]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-3318415
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
acetyl-CoA(4-)
Reaction output - small molecules:
coenzyme A(4-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-3318415