Reaction: Defective HLCS does not biotinylate ACACA:Mn2+
- in pathway: Defective HLCS causes multiple carboxylase deficiency
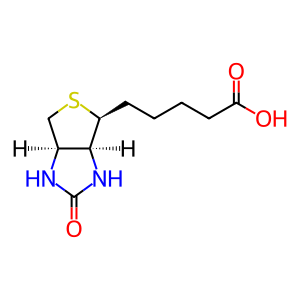
Biotin (Btn) acts as a coenzyme for 5 carboxylases that exist in their inactive apo forms. In the cytosol and mitochondrion, these apo carboxylases (apo-CBXs) are biotinylated to their active holo forms by the activity of biotin protein ligase (HCLS) (Ingaramo & Beckett 2012, Bailey et al. 2010, Hiratsuka et al. 1998). Acetyl CoA carboxylase 1 with its manganese cofactor (ACACA:Mn2+) is shown here. Defects in HLCS causes holocarboxylase synthetase deficiency (HLCS deficiency aka early-onset multiple carboxylase deficiency; MIM:253270). HLCS deficiency is an autosomal recessive disorder whereby deficient HLCS activity results in reduced activity of all 5 carboxylases. Symptoms include metabolic acidosis, organic aciduria, lethargy, hypotonia, convulsions and dermatitis. Mutations in HCLS associated with HLCS deficiency include the compound heterozygote G261Vfs*20/L237P, D571N, R508W, G581S, V550M and L216R (Suzuki et al. 1994, Yang et al. 2000, Dupuis et al. 1996, Aoki et al, 1999, Yang et al. 2001, Morrone et al. 2002).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
ATP [cytosol]
Btn [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-3323184
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
ATP(4-)
biotin
Reaction output - small molecules:
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-3323184