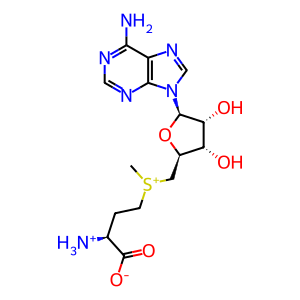
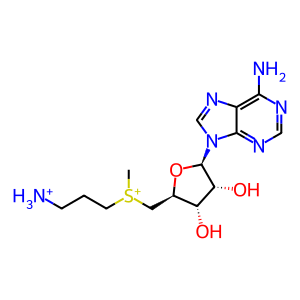
Reaction: S-Adenosyl methionine <=> Decarboxylated-Adenosyl methionine + CO2
- in pathway: Metabolism of polyamines
S-Adenosylmethionine decarboxylase belongs to a small class of amino acid decarboxylases that use a covalently bound pyruvate as a prosthetic group. It is an essential enzyme for polyamine biosynthesis and provides an important target for the design of anti-parasitic and cancer chemotherapeutic agents. It catalyzes the formation of the aminopropyl group donor in the biosynthesis of the polyamines spermidine and spermine. These pyruvoyl-dependent decarboxylases also form amines such as histamine, decarboxylated S-adenosylmethionine, phosphatidylethanolamine (a component of membrane phospholipids), and -alanine (a precursor of coenzyme A), which are all of critical importance in cellular physiology and provide important targets for drug design.
Reaction - small molecule participants:
dc-AdoMet [cytosol]
CO2 [cytosol]
AdoMet [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-351222
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
S-adenosyl-L-methionine zwitterion
Reaction output - small molecules:
S-adenosylmethioninaminium
carbon dioxide
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-351222