Reaction: Defective PAPSS2 does not transfer PO4(2-) group from ATP to APS to form PAPS
- in pathway: Defective PAPSS2 causes SEMD-PA
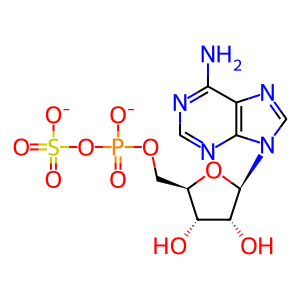
In the second step of PAPS biosynthesis, adenylyl sulfate (APS) is phosphorylated to 3'-phosphoadenylyl sulfate (PAPS), catalyzed by the APS kinase domains of the bifunctional enzymes PAPS synthases 1 and 2 (PAPSS1 and 2). PAPSS2 is essential for the sulfation of glycosaminoglycan chains of proteoglycans, a necessary post-translational modification. Defective PAPSS2 results in undersulfation of proteoglycans which causes spondyloepimetaphyseal dysplasia Pakistani type (SEMD-PA; MIM:612847), a bone disease characterized by epiphyseal dysplasia with mild metaphyseal abnormalities. Mutations resulting in SEMD-PA include S438*, T48R and R329* (Ahmad et al. 1998, ul Haque et al. 1998, Noordam et al. 2009).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
ATP [cytosol]
APS [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-3560785
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
ATP(4-)
5'-adenylyl sulfate(2-)
Reaction output - small molecules:
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-3560785