Reaction: Defective SLC26A2 does not cotransport extracellular SO4(2-), H+ to cytosol
- in pathway: Defective SLC26A2 causes chondrodysplasias
The SLC26A1 and 2 genes encode proteins that facilitate sulfate uptake into cells, though to be facilitated by cotransport with protons. SLC26A2 is ubiquitously expressed and encodes a sulfate transporter (Diastrophic dysplasia protein, DTD, DTDST) (Hastbacka et al. 1994). This transporter provides sulfate for proteoglycan sulfation which is needed for cartilage development. Defects in SLC26A2 result in impaired SO4(2-) transport leading to insufficient sulfation of cartilage proteoglycans. The severest form of achondrodysplasia, achondrogenesis type 1B (ACG-1B; MIM:600972), is caused by SLC26A2 mutations such as G255E, A585Vfs*6, L483P, R178X and N425D (Hastbacka et al. 1994, Karniski 2001, Superti-Furga et al. 1996).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
H+ [extracellular region]
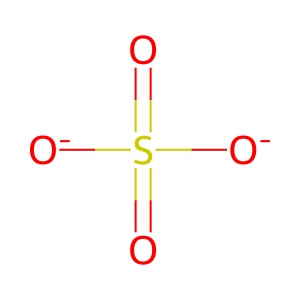
SO4(2-) [extracellular region]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-3560789
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
hydron
sulfate
Reaction output - small molecules:
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-3560789