Reaction: Type B histone acetlytransferase complex acetylates histone H4
- in pathway: HATs acetylate histones
In humans, newly synthesized histone H4 is acetylated by the cytoplasmic Type B histone acetyltransferase (HAT) complex, which is composed of RBBP7 and HAT1. This interacts with histones H4 and H2A, acetylating soluble but not nucleosomal histone H4 at lysine-6 (H4K5) and lysine-13 (H4K12) and to a lesser extent lysine-6 of histone H2A (H2AK5) (Verreault et al. 1996). The HAT1:RBBP7 complex is part of the sNASP complex, a chaperone for H3-H4 (Campos et al. 2010). HAT1 also has a role in homologous recombination repair, probably as part of a larger complex, facilitating the enrichment of H4K5/K12-acetylated H3.3 to double-strand breaks thereby marking the damaged area for subsequent recruitment of key repair factors (Yang et al. 2013).
N.B. Coordinates of post-translational modifications described here follow UniProt standard practice whereby coordinates refer to the translated protein before any further processing. Histone literature typically refers to coordinates of the protein after the initiating methionine has been removed. Therefore the coordinates of post-translated residues in the Reactome database and described here are frequently +1 when compared with the literature.
N.B. Coordinates of post-translational modifications described here follow UniProt standard practice whereby coordinates refer to the translated protein before any further processing. Histone literature typically refers to coordinates of the protein after the initiating methionine has been removed. Therefore the coordinates of post-translated residues in the Reactome database and described here are frequently +1 when compared with the literature.
Reaction - small molecule participants:
CoA-SH [nucleoplasm]
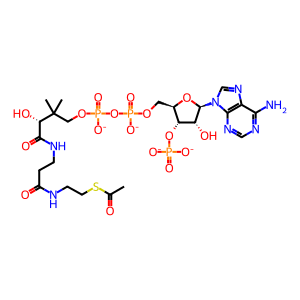
Ac-CoA [nucleoplasm]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-3662318
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
acetyl-CoA(4-)
Reaction output - small molecules:
coenzyme A(4-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-3662318