Reaction: EP300 acetylates histone H2A, H2B, H3, H4
- in pathway: HATs acetylate histones
EP300 and the related CREBBP are transcriptional regulators that interact with many other proteins. They have overlapping functions but also unique properties, particularly in vivo (Kalkhoven 2004). CREBBP and EP300 proteins are able to form a physical bridge between DNA-binding transcription factors and the RNA polymerase II complex. Histones are believed to be their main acetylation targets, but their ability to acetylate and thereby regulate transcription factors such as p53 (Gu & Roeder 1997) is also believed to be crucial (Kasper et al. 2006). EP300 can acetylate lysine-6 of histone H2A (H2AK5), lysines-12 (H2BK11), 15 (H2BK14) and to a lesser extent 5 and 20 of histone H2B, but preferentially acetylates lysines 14 and 18 of histone H3 and lysines 5 and 8 of histone H4 (Ogryzko et al. 1996, Schiltz et al. 1999). Heterozygous knockout of Ep300 is embryonic-lethal (Yao et al. 1998). Conditional knockouts have a phenotype that overlaps with that of conditional CREBBP knockouts (Kasper et al. 2006).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
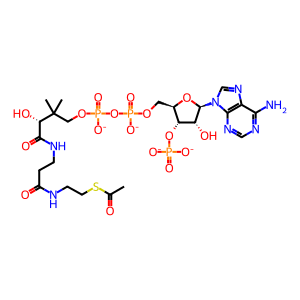
CoA-SH [nucleoplasm]
Ac-CoA [nucleoplasm]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-3662335
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
acetyl-CoA(4-)
Reaction output - small molecules:
coenzyme A(4-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-3662335