Reaction: CLOCK acetylates lysine-10 of histone H3, H4
- in pathway: HATs acetylate histones
CLOCK is a central element of the core clock mechanism that governs circadian rhythms. It has intrinsic histone acetyltransferase (HAT) activity which regulates the transcription of many clock-controlled genes (Doi et al. 2006, Hirayama et al. 2007). The carboxy-terminal region of CLOCK displays significant sequence homology with the carboxy-terminal domain of NCOA3 (ACTR), which also has intrinsic HAT activity (Chen et al. 1997). CLOCK acetylates histones H3 and H4 with greatest activity at H3K14, lesser activity at H3K9, but does not acetylate H2A and H2B (Doi et al. 2006 and Nakahata et al. 2007).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
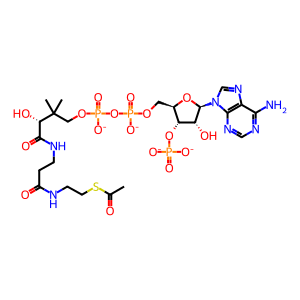
CoA-SH [nucleoplasm]
Ac-CoA [nucleoplasm]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-3697920
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
acetyl-CoA(4-)
Reaction output - small molecules:
coenzyme A(4-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-3697920