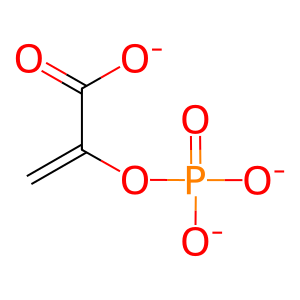
Reaction: SLC25A1 may exchange mitochondrial PEP for cytosolic anion
- in pathway: Gluconeogenesis
A variety of models assign phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) generated in the mitochondrial matrix by PCK2 (Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (GTP), mitochondrial) a role in the regulation of gluconeogenesis and its integration with other aspects of metabolism (e.g., Bluemel et al. 2021; Merrins et al. 2022; Soling et al. 1973; Yu et al. 2021). An attractive recent suggestion is that this process may specifically play a key role in regulating insulin secretion by pancreatic beta cells in response to changing blood glucose levels (Merrins et al. 2022).
Exchange of citrate for PEP across a membrane has been demonstrated in several model systems (Kleineke et al. 1973; Robinson 1971; Shug & Shrago 1973; Sul et al. 1976; Stipani et al, 1980) but the direction in which it proceeds under physiological conditions and the identity of the protein or proteins that enable this exchange remain unclear, although the citrate transporter SLC25A1 has been identified as a candidate.
Here, this hypothetical reaction is annotated as the exchange of mitochondrial PEP for an unspecified cytosolic anion, A-, possibly mediated by SLC25A1.
Exchange of citrate for PEP across a membrane has been demonstrated in several model systems (Kleineke et al. 1973; Robinson 1971; Shug & Shrago 1973; Sul et al. 1976; Stipani et al, 1980) but the direction in which it proceeds under physiological conditions and the identity of the protein or proteins that enable this exchange remain unclear, although the citrate transporter SLC25A1 has been identified as a candidate.
Here, this hypothetical reaction is annotated as the exchange of mitochondrial PEP for an unspecified cytosolic anion, A-, possibly mediated by SLC25A1.
Reaction - small molecule participants:
PEP [cytosol]
organic anion [mitochondrial matrix]
PEP [mitochondrial matrix]
organic anion [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-372449
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
phosphonatoenolpyruvate
organic anion
Reaction output - small molecules:
phosphonatoenolpyruvate
organic anion
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-372449