Reaction: GYS2 catalyzes the incorporation of phosphoglucose into glycogen-GYG2
- in pathway: Glycogen synthesis
Glycogen synthase 2 (GYS2) catalyzes the incorporation of phosphoglucose into the glycogen-GYG1 molecules with which it is associated in a cytosolic glycogen granule. This reaction occurs at a low rate, yielding approximately one molecule of glucose phosphorylated at its C2, C3, or C6 positions incorporated into a growing glycogen polymer per ten thousand glucose molecules incorporated (DePaoli-Roach et al. 2015; Irimia et al. 2015; Nitschke et al. 2013; Tagliabracci et al. 2011). The function of these small amounts of phosphoglucose in normal glycogen remains to be established. This reaction has been characterized in muscle cells, where it is catalyzed by the homologous GYS1 enzyme. The occurrence of the reaction in liver, catalyzed by GYS2, can be inferred from the fact that in the absence of the enzyme EMP2A (laforin) that removes these phosphate groups, abnormally phosphorylated glycogen accumulates in both tissues (Worby et al. 2008).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
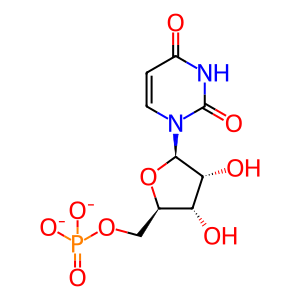
UMP [cytosol]
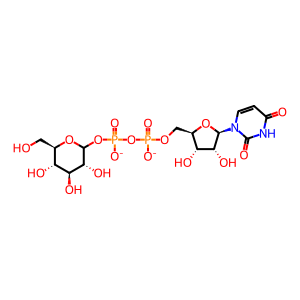
UDP-D-glucose(2-) [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-3780994
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
UDP-D-glucose(2-)
Reaction output - small molecules:
uridine 5'-monophosphate(2-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-3780994