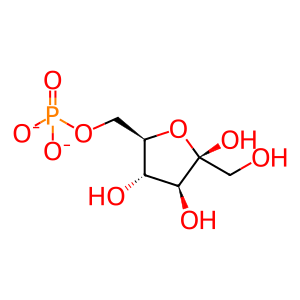
Reaction: Defective MPI does not isomerize Fru6P to Man6P
- in pathway: Defective MPI causes MPI-CDG
Mannose 6-phosphate isomerase (MPI) normally isomerises fructose 6-phosphate (Fru6P) to mannose 6-phosphate (Man6P) in the cytosol. Man6P is a precursor in the synthesis of GDP-mannose and dolichol-phosphate-mannose, required for mannosyl transfer reactions in the N-glycosylation of proteins. Defects in MPI cause congenital disorder of glycosylation 1b (MPI-CDG, previously known as CDG1b,; MIM:602579), a multisystem disorder characterised by under-glycosylated serum glycoproteins (Schollen et al. 2000). Unlike PMM2-CDG (CDG1a), there is no neurological involvement with MPI-CDG. Instead, patients present predominantly with diarrhoea, failure to thrive and protein-losing enteropathy (Pelletier et al. 1986). MPI-CDG is one of two CDGs that can be treated with oral mannose supplementation, but can be fatal if left untreated (Marquardt & Denecke 2003). MPI mutations causing MPI-CDG are R219Q, S102L, M138T, R295H and A38Gfs*26 (Niehues et al. 1998, Schollen et al. 2000, Jaeken et al. 1998, Vuillaumier-Barrot et al. 2002).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
Fru(6)P [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-3781832
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
beta-D-fructofuranose 6-phosphate(2-)
Reaction output - small molecules:
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-3781832