Reaction: HDAC8 deacetylates histones
- in pathway: HDACs deacetylate histones
HDAC8 can catalyze the in vitro deacetylation of a number of acetylated histone variants including full-length H2A/H2B, H3, and H4 histones acetylated at nonspecific lysines (Hu et al. 2000, Buggy et al. 2000). Peptide sequences corresponding to the H4 histone tail with an acetylated lysine at position sixteen (AcK16) were also identified as in vitro substrates (Buggy et al. 2000, Van der Wyngaert et al. 2000). Subsequent studies have used the H4 histone tail sequence as a peptide template to investigate the amino acid sequence preference of HDAC8. HDAC8 can catalyze the in vitro deacetylation of AcK20 on the H4 histone tail though at a much slower rate than deacetylation of AcK16 peptides (Dose et al. 2011). HDAC8 can catalyze deacetylation in vivo in the absence of a protein complex (Dowling et al. 2010). The role of HDAC8 in catalyzing deacetylation of specific sites in histones in vivo remains unclear (Wolfson et al. 2013).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
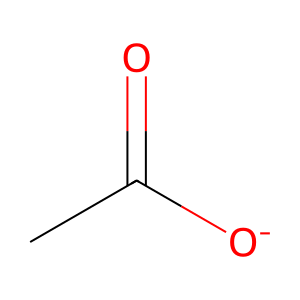
acetate [nucleoplasm]
H2O [nucleoplasm]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-3782637
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
water
Reaction output - small molecules:
acetate
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-3782637