Reaction: glyoxylate + alanine => glycine + pyruvate [peroxisome]
- in pathway: Glyoxylate metabolism and glycine degradation
Alanine-glyoxylate transaminase (AGXT) catalyzes the irreversible reaction of glyoxylate and alanine to form glycine and pyruvate (Danpure and Jennings 1988). The active form of the enzyme is a homodimer (Zhang et al. 2003) with one molecule of pyridoxal phosphate bound to each subunit (Coulter-Mackie et al. 2005). Mutations in this enzyme are associated with primary hyperoxaluria type I. Mutant alleles encode both catalytically inactive proteins and active ones that are mis-localized to mitochondria (Purdue et al. 1990; Takada et al. 1990).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
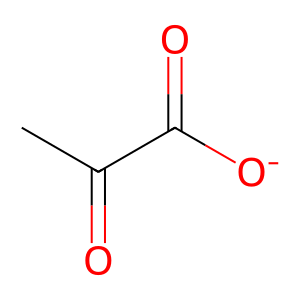
PYR [peroxisomal matrix]
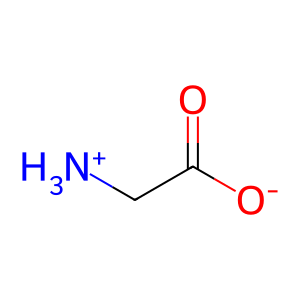
Gly [peroxisomal matrix]
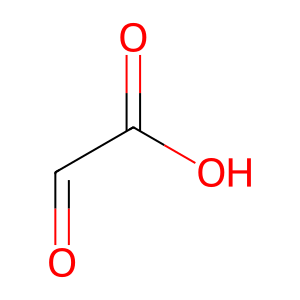
glyoxylate [peroxisomal matrix]
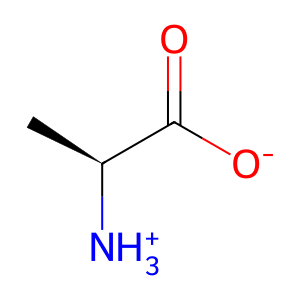
L-Ala [peroxisomal matrix]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-389684
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
glyoxylic acid
L-alanine zwitterion
Reaction output - small molecules:
pyruvate
glycine zwitterion
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-389684