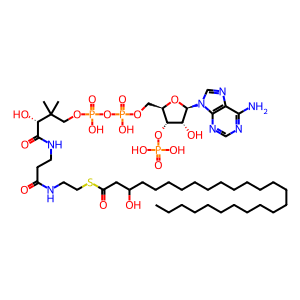
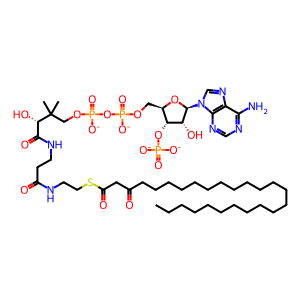
Reaction: HSD17B4 dehydrogenates 3-hydroxyhexacosanoyl-CoA
- in pathway: Beta-oxidation of very long chain fatty acids
Peroxisomal HSD17B4 dimer catalyzes the reaction of 3-hydroxyhexacosanoyl-CoA and NAD+ to form 3-ketohexacosanoyl-CoA and NADH + H+. The enzyme is bifunctional - an aminoterminal domain catalyzes the dehydrogenation of a variety of 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA's, the reaction annotated here, and a carboxyterminal domain catalyzes the hydration of a variety of trans-2,3-dehydroacyl-CoA's (Jiang et al. 1996, 1997). Defects in the enzyme are associated with a severe disorder of peroxisomal fatty acid metabolism in humans (Ferdinandusse et al. 2006).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
H+ [peroxisomal matrix]
3-ketohexacosanoyl-CoA [peroxisomal matrix]
NADH [peroxisomal matrix]
3-hydroxyhexacosanoyl-CoA [peroxisomal matrix]
NAD+ [peroxisomal matrix]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-390251
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
3-hydroxyhexacosanoyl-CoA
NAD(1-)
Reaction output - small molecules:
hydron
3-oxohexacosanoyl-CoA(4-)
NADH(2-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-390251