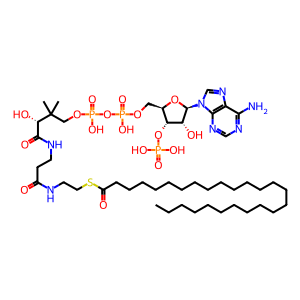
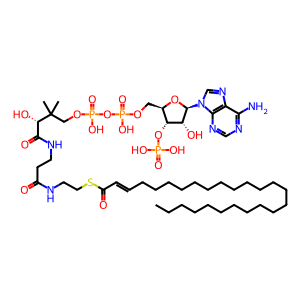
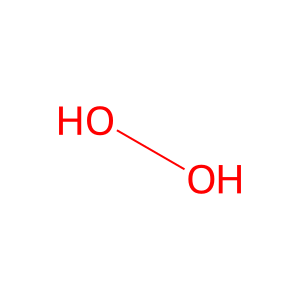
Reaction: hexacosanoyl-CoA + O2 => trans-2,3-dehydrohexacosanoyl-CoA + H2O2
- in pathway: Beta-oxidation of very long chain fatty acids
Peroxisomal ACOX1 catalyzes the reaction of hexacosanoyl-CoA and O2 to form trans-2,3-dehydrohexacosanoyl-CoA and H2O2. The active form of the enzyme is a homodimer with FAD as a cofactor (Chu et al. 1995). Mutations in the ACOX1 gene are asociated with accumulation of very long chain fatty acids. Two isoforms of ACOX1, generated by alternative splicing are known; a mutation affecting specifically the second isoform blocks the oxidation of very long chain fatty acids (Ferdinandusse et al. 2007).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
trans-2,3-dehydrohexacosanoyl-CoA [peroxisomal matrix]
H2O2 [peroxisomal matrix]
O2 [peroxisomal matrix]
C26:0 CoA [peroxisomal matrix]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-390256
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
dioxygen
hexacosanoyl-CoA
Reaction output - small molecules:
trans-2-hexacosenoyl-CoA
hydrogen peroxide
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-390256