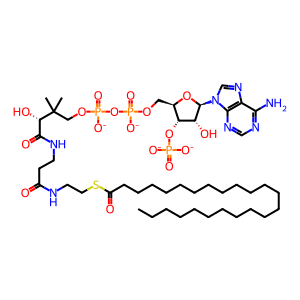
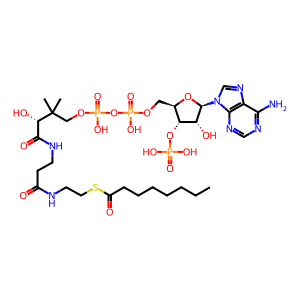
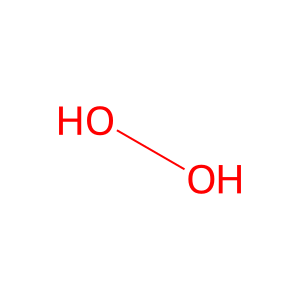
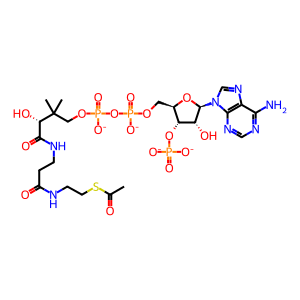
Reaction: tetracosenoyl-CoA + 8 O2 + 8 H2O + 8 NAD+ + 8 CoASH => octanoyl-CoA + 8 H2O2 + 8 NADH + 8 H+ + 8 acetyl-CoA
- in pathway: Beta-oxidation of very long chain fatty acids
In eight cycles of beta-oxidation mediated by the same enzyme activities responsible for the conversion of hexacosanoyl-CoA to tetracosenoyl-CoA, the latter molecule is converted to octanoyl-CoA. Eight molecules each of O2, H2O, NAD+, and CoASH are consumed in the process and eight molecules of H2O2 and NADH + H+ are generated, together with eight molecules of acetyl-CoA (Wanders and Waterham 2006).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
H+ [peroxisomal matrix]
Octanoyl-CoA [peroxisomal matrix]
H2O2 [peroxisomal matrix]
Ac-CoA [peroxisomal matrix]
NADH [peroxisomal matrix]
O2 [peroxisomal matrix]
H2O [peroxisomal matrix]
CoA-SH [peroxisomal matrix]
tetracosanoyl-CoA [peroxisomal matrix]
NAD+ [peroxisomal matrix]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-390302
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
dioxygen
water
coenzyme A(4-)
tetracosanoyl-CoA(4-)
NAD(1-)
Reaction output - small molecules:
hydron
octanoyl-CoA
hydrogen peroxide
acetyl-CoA(4-)
NADH(2-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-390302