Reaction: HRH1 binds hist
- in pathway: Histamine receptors
The histamine H1 receptor (De Backer MD et al, 1993) is found on smooth muscle, endothelium and the CNS. Histamine released from neurons binds to the H1 receptor and causes systemic vasodilation and increased endothelial cell permeability. The effects are modulated by the activated receptor binding to the G protein alpha-q/11 subtype which can activate phospholipase C and the phosphatidylinositol (PIP2) signaling pathway (Tilly BC et al, 1990). The classical antihistamines (histamine H1 receptor antagonists) were developed in the early 1930s and were shown to reduce the effects of histamine on many tissues.
Reaction - small molecule participants:
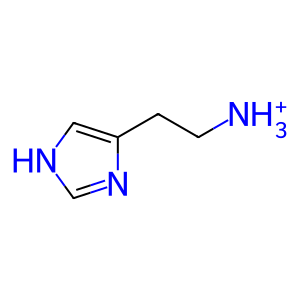
Hist [extracellular region]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-390912
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
histaminium
Reaction output - small molecules:
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-390912