Reaction: Oxoeicosanoid receptor can bind oxoeicosanoid
- in pathway: Eicosanoid ligand-binding receptors
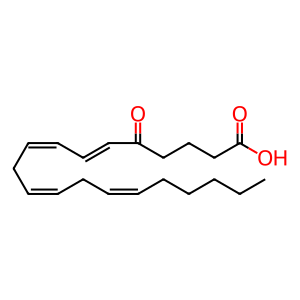
Oxoeicosanoids are a family of biologically active arachidonic acid derivatives that are associated with cellular migration. These mediators are potent chemotaxins for eosinophils, monocytes and polymorphonuclear neutrophils. They act via the OXE receptor (Hosoi T et al, 2002), expressed principally in kidney, liver as well as in eosinophils, neutrophils, and lung macrophages. The most potent ligand is 5-oxo-6,8,11,14-eicosatetraenoic acid (5-oxo-ETE). Activation of the receptor leads to calcium mobilization and the receptor was shown to be coupled to the G alpha i subunit (Jones CE et al, 2003).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
5-oxoETE [extracellular region]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-391905
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
5-oxo-ETE
Reaction output - small molecules:
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-391905