Reaction: TP receptor can bind thromboxane
- in pathway: Prostanoid ligand receptors
Thromboxane (TBXA2) is a potent stimulator for platelet aggregation and clot formation and also plays a role in vascular tone. The thromboxane receptor TP (Hirata et al. 1991) is found on the surface of vascular endothelium, platelets and in the placenta. Once bound to its ligand, TP's effects are mediated via coupling to G q/11 activation of a phosphatidylinositol-calcium second messenger system (Kinsella BT et al, 1997). TP signaling also involves G12/13 signaling; selective activation of G12/13 results in dense granule release in a mechanism that is independent of Gq/phospholipase C. The downstream mechanism for this is thought to be RhoA mediated activation of PKCdelta, as PAR-mediated dense granule release is inhibited if RhoA is blocked, and RhoA regulates PKCdelta T505 phosphorylation (Jin et al. 2009).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
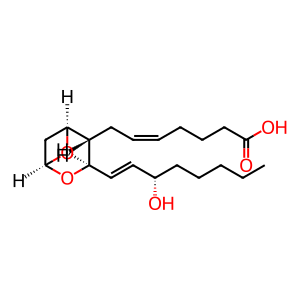
TXA2 [extracellular region]
TXA2 [extracellular region]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-391939
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
thromboxane A2
thromboxane A2
Reaction output - small molecules:
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-391939