Reaction: BLT receptors can bind LTB4
- in pathway: Leukotriene receptors
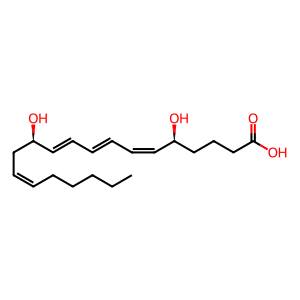
The dihydroxy-leukotriene, leukotriene B4 (LTB4) stimulates neutrophil chemotaxis and secretion. Chemotaxis, the principal effects of LTB4 and related dihydroxy-acids on leukocytes, occurs via activation of BLT (1 and 2) receptors (Yokomizo T et al, 1997; Yokozimo T et al, 2000). BLT2 is expressed ubiquitously, in contrast to BLT1, which is expressed predominantly in leukocytes. These receptors mediate their actions by coupling to G protein alpha q/11 subunits (McLeish KR et al, 1989) which activate a phosphatidylinositol-calcium second messenger system.
Reaction - small molecule participants:
LTB4 [extracellular region]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-391941
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
leukotriene B4
Reaction output - small molecules:
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-391941