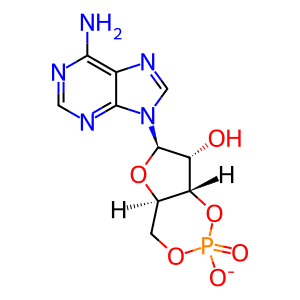
Reaction: Adenylate cyclase converts ATP to 3',5'-cyclic AMP (cAMP) and pyrophosphate
- in pathway: G alpha (z) signalling events
The activation of adenylyl (adenylate) cyclase (AC) results in the production of adenosine-3',5'-monophosphate i.e. cyclic AMP. Humans have 9 genes encoding membrane-associated AC and one encoding a soluble AC. Two of the classes of heterotrimeric G-proteins are named according to their effect on AC; G(s) stimulates all membrane-bound ACs (the s in G(s) denotes AC stimulatory); the G(i) class inhibits some AC isoforms, particularly 5 and 6. Beta-gamma subunits of heterotrimeric G-proteins can also regulate AC. Ca2+/Calmodulin activates some AC isoforms (1, 8 and 3) but is inhibitory to others (5 and 6).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
PPi [cytosol]
cAMP [cytosol]
ATP [cytosol]
PPi [cytosol]
cAMP [cytosol]
ATP [cytosol]
PPi [cytosol]
cAMP [cytosol]
ATP [cytosol]
PPi [cytosol]
cAMP [cytosol]
ATP [cytosol]
PPi [cytosol]
cAMP [cytosol]
ATP [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-392129
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
ATP(4-)
ATP(4-)
ATP(4-)
ATP(4-)
ATP(4-)
Reaction output - small molecules:
diphosphate(3-)
3',5'-cyclic AMP(1-)
diphosphate(3-)
3',5'-cyclic AMP(1-)
diphosphate(3-)
3',5'-cyclic AMP(1-)
diphosphate(3-)
3',5'-cyclic AMP(1-)
diphosphate(3-)
3',5'-cyclic AMP(1-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-392129