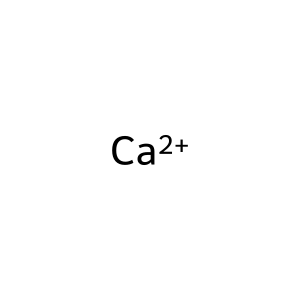Reaction: Activation of Ca permeable AMPA receptors
- in pathway: Activation of AMPA receptors
Each AMPA receptor subunit binds one glutamate molecule in the ligand binding site in the N terminus. Each receptor is capable of binding four glutamate molecule, however, channel opens when two sites are occupied by the ligand and the current increases with increased ligand binding. Ca permeable AMPA receptors containing homomers of GluR1 or heteromers containing GluR1, GluR3 and GluR4 conduct Ca upon glutamate or agonist namely AMPA (alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid) binding. Calcium permeable AMPA receptors conduct Ca and other cations such as Na. The inonic flux leads to Ca or Na currents that leads to either increase in the intracellular Ca concentration leading to further Ca-dependent signaling or increase in depolarization that opens voltage gated channels such as NMDA receptors that require both membrane depolarization and glutamate binding for activation.
Reaction - small molecule participants:
Ca2+ [cytosol]
Ca2+ [extracellular region]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-399712
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
calcium(2+)
Reaction output - small molecules:
calcium(2+)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-399712