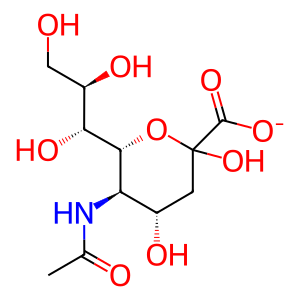
Reaction: NEU3 hydrolyzes Neu5Ac from glycoconjugates
- in pathway: Sialic acid metabolism
Sialidases 1-4 (NEU1-4, neuraminidases, receptor-destroying enzymes, RDEs) hydrolyze sialic acids (N-acetylneuraminic acid, Neu5Ac) to produce asialo compounds, a step in the degradation process of glycoproteins and gangliosides and are expressed in a variety of cellular locations. NEU3 localizes to the plasma membrane and hydrolyses Neu5Ac especially from gangliosides with alpha2,3- or alpha2,8-linkages present in the lipid bilayer (Wada et al. 1999, Monti et al. 2000). By regulating the composition of the lipid bilayer, NEU3 has been identified as an important regulator of trans-membrane signaling (Miyagi et al. 2008).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
Neu5Ac [cytosol]
H2O [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-4084994
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
water
Reaction output - small molecules:
N-acetylneuraminate
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-4084994