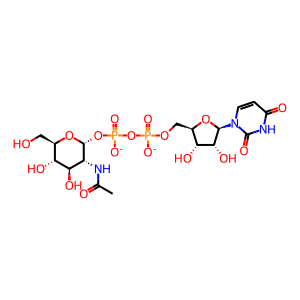
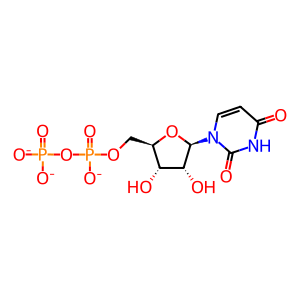
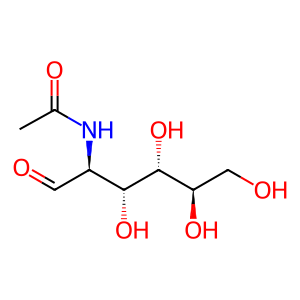
Reaction: GNE hydrolyzes/epimerises UDP-GlcNAc to ManNAc and UDP
- in pathway: Sialic acid metabolism
UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase, N-acetylmannosamine kinase (GNE) is a bifunctional enzyme in the cytosol that is involved in the first two critical, rate-limiting steps of sialic acid (Neu5Ac, N-acetylneuraminic acid) biosynthesis, a main constituent of glycoconjugates. Because Neu5Ac is found at terminal positions of glycoconjugates, this molecule is involved in most cell-cell or cell-extracellular matrix interactions, serving as recognition sites. Thus, Neu5Ac plays critical roles in health and disease. In the first reaction, GNE hydrolyses and epimerises UDP-N-acetylglucosamine (UDP-GlcNAc) to N-acetylmannosamine (ManNAc) (Lucka et al. 1999, Keppler et al. 1999).
There are various disorders associated with defects in the GNE gene. Defects in GNE can cause sialuria (MIM:269921), an inborn error of metabolism characterised by cytoplasmic accumulation and increased urinary excretion of Neu5Ac (Seppala et al. 1999). Mutations causing sialuria are R266W, R266Q and R263L (Seppala et al. 1999). Defects in GNE can also cause hereditary inclusion body myopathy (IBM2; MIM:600737), an autosomal recessive neuromuscular disorder characterised by adult-onset, progressive distal and proximal muscle weakness and wastage. Muscle pathology shows rimmed vacuoles and filamentous inclusions (Eisenberg et al. 2001). The common M712T mutation can cause IBM2, as well as heterozygosity with the mutation M171V (Eisenberg et al. 2001, Argov et al. 2003, Broccolini et al. 2002). Defects in GNE can also cause Nonaka myopathy (NM; MIM:605820), an early adulthood-onset muscular disorder characterised by weakness and wastage of the lower limbs and rimmed vacuoles (Nonaka et al. 1981, Eisenberg et al. 2001). Mutations causing NK include the common V572L, either homozygous or heterozygous with C303V (Tomimitsu et al. 2002, Kayashima et al. 2002) and the heterozygous M712T with A631V indicated that NK and IBM2 are allelic, if not identical, disorders (Tomimitsu et al. 2004).
There are various disorders associated with defects in the GNE gene. Defects in GNE can cause sialuria (MIM:269921), an inborn error of metabolism characterised by cytoplasmic accumulation and increased urinary excretion of Neu5Ac (Seppala et al. 1999). Mutations causing sialuria are R266W, R266Q and R263L (Seppala et al. 1999). Defects in GNE can also cause hereditary inclusion body myopathy (IBM2; MIM:600737), an autosomal recessive neuromuscular disorder characterised by adult-onset, progressive distal and proximal muscle weakness and wastage. Muscle pathology shows rimmed vacuoles and filamentous inclusions (Eisenberg et al. 2001). The common M712T mutation can cause IBM2, as well as heterozygosity with the mutation M171V (Eisenberg et al. 2001, Argov et al. 2003, Broccolini et al. 2002). Defects in GNE can also cause Nonaka myopathy (NM; MIM:605820), an early adulthood-onset muscular disorder characterised by weakness and wastage of the lower limbs and rimmed vacuoles (Nonaka et al. 1981, Eisenberg et al. 2001). Mutations causing NK include the common V572L, either homozygous or heterozygous with C303V (Tomimitsu et al. 2002, Kayashima et al. 2002) and the heterozygous M712T with A631V indicated that NK and IBM2 are allelic, if not identical, disorders (Tomimitsu et al. 2004).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
UDP [cytosol]
ManNAc [cytosol]
H2O [cytosol]
UDP-GlcNAc [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-4085021
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
water
UDP-N-acetyl-alpha-D-glucosamine(2-)
Reaction output - small molecules:
UDP(3-)
aldehydo-N-acetyl-D-mannosamine
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-4085021