Reaction: Defective GFPT1 does not transfer an amino group from L-Gln to F6P to form GlcN6P
- in pathway: Defective GFPT1 causes CMSTA1
Glucosamine-fructose 6-phosphate aminotransferases 1 and 2 (GFPT1,2) are the first and rate-limiting enzymes in the hexosamine synthesis pathway, and thus formation of hexosamines like N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc). These enzymes probably play a role in limiting the availability of substrates for the N- and O-linked glycosylation of proteins. GFPT1 and 2 are required for normal functioning of neuromuscular synaptic transmission. Defects in GFPT1 cause myasthenia, congenital, with tubular aggregates 1 (CMSTA1; MIM:610542), characterised by altered muscle fibre morphology and impaired neuromuscular junction development (Senderek et al. 2011). The missense mutations observed do not always result in significant reduction in enzyme activity, but biopsies show reduced amounts of GFPT1 protein suggesting increased turnover or defective translation (Senderek et al. 2011). Example mutations are R111C, W240*, D348Y, T15A and T147Qfs*61 (Senderek et al. 2011).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
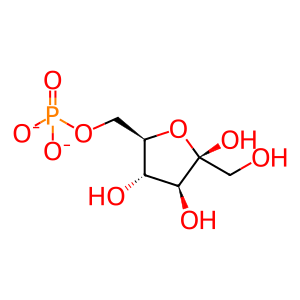
Fru(6)P [cytosol]
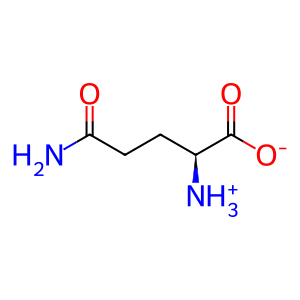
L-Gln [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-4085027
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
beta-D-fructofuranose 6-phosphate(2-)
L-glutamine zwitterion
Reaction output - small molecules:
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-4085027