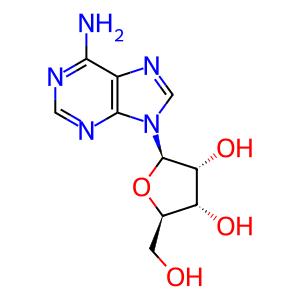
Reaction: A1 and A3 receptors bind adenosine
- in pathway: Adenosine P1 receptors
The A1 receptor (Libert F et al, 1992) has an inhibitory function on most of the tissues in which it is expressed. In the brain, it slows metabolic activity and also decreases heart rate. The A1, together with A2a receptors, are believed to play a role in regulating myocardial oxygen consumption and coronary blood flow.
The A3 receptor (Salvatore CA et al, 1993) mediates a sustained cardioprotective function during cardiac ischemia and it is involved in the inhibition of neutrophil degranulation in neutrophil-mediated tissue injury.
Both the A1 and A3 receptors mediate their effects by coupling with the G protein alpha i subunit which inhibits adenylyl cyclase (Wise A et al, 1999).
The A3 receptor (Salvatore CA et al, 1993) mediates a sustained cardioprotective function during cardiac ischemia and it is involved in the inhibition of neutrophil degranulation in neutrophil-mediated tissue injury.
Both the A1 and A3 receptors mediate their effects by coupling with the G protein alpha i subunit which inhibits adenylyl cyclase (Wise A et al, 1999).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
Ade-Rib [extracellular region]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-418904
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
adenosine
Reaction output - small molecules:
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-418904