Reaction: GABAB heterodimeric receptor binds GABA
- in pathway: GABA B receptor activation
Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) is the chief inhibitory neurotransmitter in the mammalian central nervous system. GABA exerts its effects through two ligand-gated channels and a the GPCR GABAB (Kaupmann K et al, 1998), which acts through G proteins to regulate potassium and calcium channels. GABAB can only bind GABA once it forms a heterodimer composed of the GABABR1 and GABABR2 receptors (White JH et al, 1998). The effects of this dimer are mediated by coupling to the G protein alpha i subunit, which inhibits adenylyl cyclase (Odagaki & Koyama 2001).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
GABA [extracellular region]
GABA [extracellular region]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-420688
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
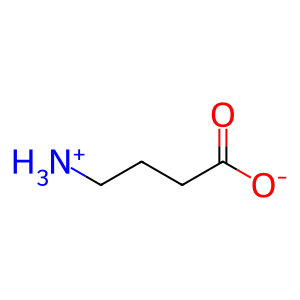
gamma-aminobutyric acid zwitterion
gamma-aminobutyric acid zwitterion
Reaction output - small molecules:
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-420688