Reaction: SLC26A1,2 cotransport SO4(2-), H+ from extracellular region to cytosol
- in pathway: Transport and synthesis of PAPS
The SLC26A1 and 2 genes encode proteins that facilitate sulfate (SO4(2-)) uptake into cells (Alper & Sharma 2013). The mechanism by which these transporters work is unclear but may be enhanced by extracellular halides or acidic pH environments, cotransporting protons electroneutrally. Both can transport SO4(2-) (as well as oxalate and Cl-) across the basolateral membrane of epithelial cells. SLC26A1 encodes the sulfate anion transporter 1 (SAT1) (Regeer et al. 2003) and is most abundantly expressed in the liver and kidney, with lower levels expressed in many other parts of the body. SLC26A2 is ubiquitously expressed and encodes a sulfate transporter (Diastrophic dysplasia protein, DTD, DTDST) (Hastbacka et al. 1994). This transporter provides sulfate for sulfation of glycosaminoglycan chains in proteoglycans needed for cartilage development. Defects in SLC26A2 are implicated in the pathogenesis of several human chondrodysplasias.
Reaction - small molecule participants:
H+ [cytosol]
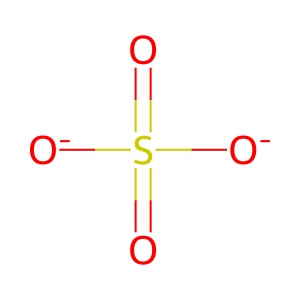
SO4(2-) [cytosol]
H+ [extracellular region]
SO4(2-) [extracellular region]
H+ [cytosol]
SO4(2-) [cytosol]
H+ [extracellular region]
SO4(2-) [extracellular region]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-427555
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
hydron
sulfate
hydron
sulfate
Reaction output - small molecules:
hydron
sulfate
hydron
sulfate
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-427555