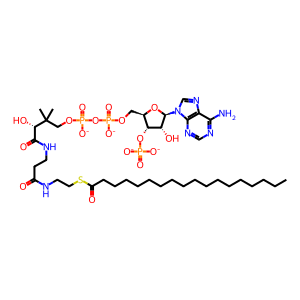
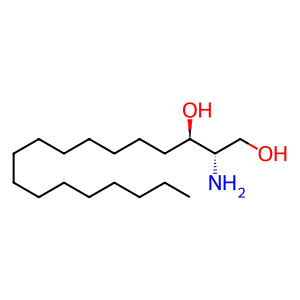
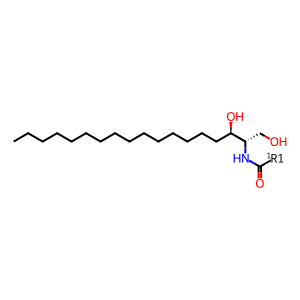
Reaction: sphinganine + stearyl-CoA => dihydroceramide + CoASH
- in pathway: Sphingolipid de novo biosynthesis
LASS (longevity assurance homolog, also known as ceramide synthase, CerS) enzymes associated with the endoplasmic reticulum membrane catalyze the reaction of sphinganine (dihydrosphingosine) and a long-chain fatty acyl CoA such as stearyl-CoA to form a dihydroceramide and CoASH (Pewzner-Jung et al. 2006). Six human LASS genes have been identified; they differ in the identities of the fatty acyl CoAs that they use most efficiently as substrates (Lahiri and Futerman 2005; Laviad et al. 2008).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
DHCE [endoplasmic reticulum membrane]
CoA-SH [cytosol]
ST-CoA [cytosol]
SPA [endoplasmic reticulum membrane]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-428185
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
stearoyl-CoA(4-)
sphinganine
Reaction output - small molecules:
N-acylsphinganine
coenzyme A(4-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-428185