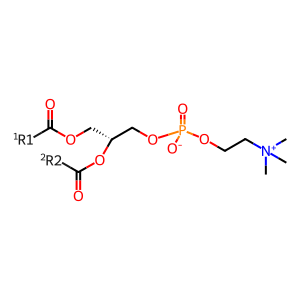
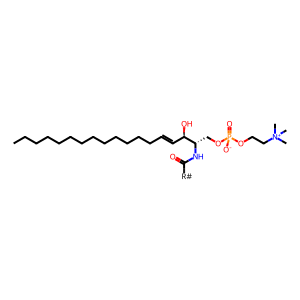
Reaction: phosphatidylcholine + ceramide <=> sphingomyelin + diacylglycerol [SGMS2]
- in pathway: Sphingolipid de novo biosynthesis
SGMS2 (sphingomyelin synthase 2) catalyzes the reversible reaction of phosphatidylcholine and ceramide to form sphingomyelin and diacylglycerol. Most SGMS2 actitiy is associated with the plasma membrane, although active enzyme is also present in the Golgi apparatus (Tafesse et al. 2007; Villani et al. 2008; Ding et al. 2008). Phosphatidylcholine was identified as the source of the phosphocholine moiety donated to ceramide in this reaction, in studies of the mouse enzyme in the 1970s (Diringer et al. 1972; Ullman and Radin 1974). Palmitoylation of at least two cysteine residues near the carboxy terminus of SGMS2 appears to be required for association of the protein with the plasma membrane (Tani and Kuge 2009). SGMS2 is widely expressed in the body and while studies of cultured cells indicate that this is a minor source of cellular sphingomyelin, blockage of SGMS2 activity inhibits cell growth (Huitema et al. 2004; Tafesse et al. 2007).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
SPHM [plasma membrane]
DAGs [plasma membrane]
PC [plasma membrane]
CERA [plasma membrane]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-429786
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
1,2-diacyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine
N-acylsphingoid
Reaction output - small molecules:
sphingomyelin d18:1
diglyceride
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-429786