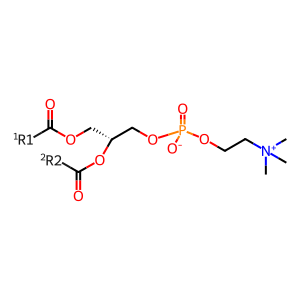
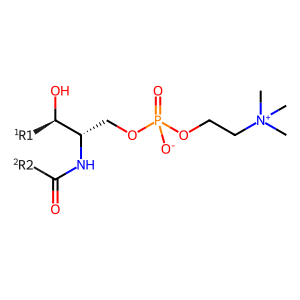
Reaction: phosphatidylcholine + ceramide <=> sphingomyelin + diacylglycerol [SGMS1]
- in pathway: Sphingolipid de novo biosynthesis
SGMS1 (sphingomyelin synthase 1) associated with the membrane of the Golgi apparatus catalyzes the reversible reaction of phosphatidylcholine and ceramide to form sphingomyelin and diacylglycerol. Phosphatidylcholine was identified as the source of the phosphocholine moiety donated to ceramide in this reaction, in studies of the mouse enzyme in the 1970s (Diringer et al. 1972; Ullman and Radin 1974). SGMS1 is widely expressed in the body and studies of cultured cells indicate that this reaction provides the major source of cellular sphingomyelin (Yamaoka et al. 2004; Huitema et al. 2004; Tafesse et al. 2007).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
DAGs [Golgi membrane]
SPHM [Golgi membrane]
PC [Golgi membrane]
CERA [Golgi membrane]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-429798
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
1,2-diacyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine
N-acylsphingoid
Reaction output - small molecules:
diglyceride
sphingomyelin
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-429798