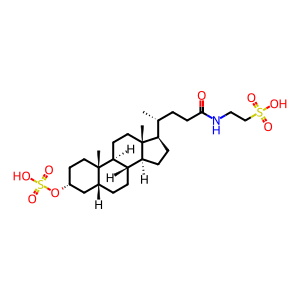
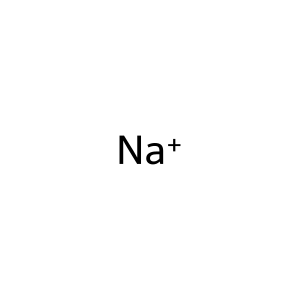Reaction: SOAT can transport taurolithocholate-3-sulphate
The human SLC10A6 gene encodes a sodium-dependant organic anion transporter, SOAT. Highest expressions of the gene are in testis, placenta and pancreas. Unlike the other SLC10A gene products, SOAT shows no affinity for binding bile acids. However, SOAT is able to transport sulpho-conjugated bile acids such as taurolithocholate 3-sulphate (Geyer J et al, 2007). It can also transport the structurally similar sulphated steroids (not shown here), thus SOAT may play a role in delivery of these prohormones to testis, pancreas and placenta.
Reaction - small molecule participants:
Na+ [cytosol]
taurolithocholate sulfate [cytosol]
taurolithocholate sulfate [extracellular region]
Na+ [extracellular region]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-433089
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
taurolithocholic acid sulfate
sodium(1+)
Reaction output - small molecules:
sodium(1+)
taurolithocholic acid sulfate
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-433089