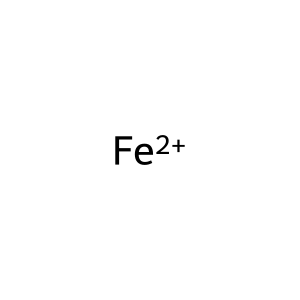Reaction: SLC11A2 cotransports Fe2+, H+ from extracellular region to cytosol
- in pathway: Iron uptake and transport
The primary site for absorption of dietary iron is the duodenum. Ferrous iron (Fe2+) is taken up from the gut lumen across the apical membranes of enterocytes and released into the portal vein circulation across basolateral membranes. The human gene SLC11A2 encodes the divalent cation transporter DCT1 (NRAMP2, Natural resistance-associated macrophage protein 2). DCT1 resides on the apical membrane of enterocytes and mediates the uptake of many metal ions, particularly ferrous iron, into these cells (Tandy et al. 2000).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
H+ [cytosol]
Fe2+ [cytosol]
H+ [extracellular region]
Fe2+ [extracellular region]
H+ [cytosol]
Fe2+ [cytosol]
H+ [extracellular region]
Fe2+ [extracellular region]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-435349
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
hydron
iron(2+)
hydron
iron(2+)
Reaction output - small molecules:
hydron
iron(2+)
hydron
iron(2+)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-435349