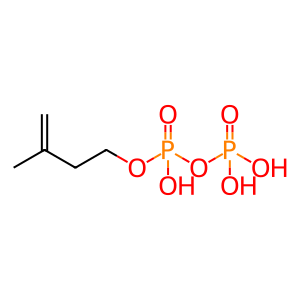
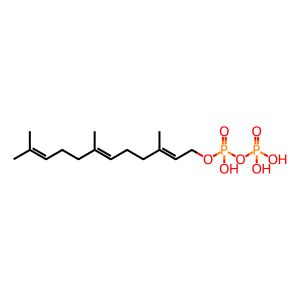
Reaction: DHDDS:NUS1 elongates E,E-FPP with (n)IPPP to form pPPP
- in pathway: Synthesis of Dolichyl-phosphate
The ER membrane-associated enzyme dehydrodolichyl diphosphate synthase (DHDDS) mediates the sequential head-to-tail cis addition of multiple isopentyl pyrophosphate (IPP) molecules to farnesyl pyrophosphate (E,E-FPP) to produce polyprenol pyrophosphate (pPPP) (Shridas et al. 2003). Dolichol in humans contain homologues ranging from 17-23 isoprene units, the most common homologues contain 19 or 20 isoprene units (Freeman et al. 1980). Dehydrodolichyl diphosphate syntase complex subunit NUS1 (NUS1, aka Nogo-B receptor NgBR) interacts with DHDDS, enhancing its stability and promoting Dol-P production (Harrison et al. 2011).
Defects in DHDDS cause retinitis pigmentosa 59 (RP59; MIM:613861), a pigment retinopathy, characterised by retinal pigment deposits (visible on fundus examination) and primary loss of rod photoreceptors followed by secondary loss of cone photoreceptors. Sufferers typically have night vision blindness and loss of mid to peripheral vision. As the condition progresses, they lose far peripheral vision and eventually central vision (Zuchner et al. 2011).
Defects in DHDDS cause retinitis pigmentosa 59 (RP59; MIM:613861), a pigment retinopathy, characterised by retinal pigment deposits (visible on fundus examination) and primary loss of rod photoreceptors followed by secondary loss of cone photoreceptors. Sufferers typically have night vision blindness and loss of mid to peripheral vision. As the condition progresses, they lose far peripheral vision and eventually central vision (Zuchner et al. 2011).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
pPPP [integral component of cytoplasmic side of endoplasmic reticulum membrane]
IPPP [cytosol]
E,E-FPP [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-4419978
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
isopentenyl diphosphate
2-trans,6-trans-farnesyl diphosphate
Reaction output - small molecules:
polyprenyl diphosphate
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-4419978