Reaction: Calmodulin-activated adenylate cyclases ADCY1 and ADCY8 generate cAMP
Based on studies in rat neurons, Ca2+ influx through NMDA receptors in the post-synaptic neuron results in activation of adenylate cyclase (Chetkovich et al. 1991), which is mediated by binding of activated calmodulin (CALM1:4xCa2+) to adenylate cyclase (Chetkovich and Sweatt 1993). Two adenylate cyclase isoforms, ADCY1 (AC1) and ADCY8 (AC8), are activated by calmodulin and involved in NMDA receptor-mediated long term potentiation (LTP), which plays a role in learning and memory (Xia et al. 1991, Cali et al. 1994, Wong et al. 1999, Wei et al. 2002, Nicol et al. 2005, Conti et al. 2007). Activated ADCY1 and ADCY8 produce cAMP, which further activates PKA.
Reaction - small molecule participants:
PPi [cytosol]
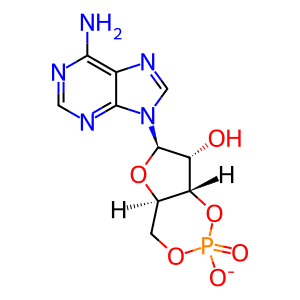
cAMP [cytosol]
ATP [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-442715
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
ATP(4-)
Reaction output - small molecules:
diphosphate(3-)
3',5'-cyclic AMP(1-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-442715